ATOMS AND
MOLECULES
1) Laws of
chemical combination :-
i) Law of conservation of mass :- states that ‘Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in
a chemical reaction’.
This means that during a
chemical reaction the sum of the masses of the reactants and products remain
unchanged.
Activity :-
Take some sodium sulphate
solution in a conical flask and some barium chloride solution in an ignition tube.
Hang the ignition tube in the flask by a thread and pot a cork on the flask.
Find the mass of the flask on a balance. Then tilt the flask. A chemical
reaction takes place and sodium chloride and barium sulphate are formed. Then
find the mass of the flask again. It will be seen that the sum of the masses of
the reactants and products remain unchanged.
ii) Law of constant proportions :- states that ‘ In a chemical
compound the elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass’.
Eg :- Water ( H2O)
always contains two elements hydrogen and oxygen combined together in the same
ratio of 2:16 or 1:8 by mass. If 9 g of water is decomposed we get 1 g of
hydrogen and 8 g of oxygen.
Ammonia (NH3) always
contains two elements nitrogen and hydrogen combined together in the same ratio
of 14:3 by mass.
2) Dalton’s atomic theory :-
i)
Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms.
ii) Atoms are indivisible and cannot be
created or destroyed in a chemical
reaction
iii) Atoms of a given element are similar in mass and properties.
iv) Atoms of different elements have
different masses and properties.
v) Atoms combine in small whole number ratios
to form compounds.
vi) In a given compound the relative
number and kind of atoms are constant.
3) Atom :-
An atom is the
smallest particle of an element that may or may not exist independently and
retains all its chemical properties.
Atoms are very small in size and
smaller than anything we can imagine or compare with.
Atomic radius is measured in
nanometres (nm)
1 nanometer = 10 -9 m
or 1 meter = 109 nm
Eg :- The atomic radius of an atom of hydrogen is 10-10 m.
The radius of a molecule
of water is 10-9 m.
 |
| from google images |

4) Symbols of atoms of different elements :-
The symbols of
elements are represented by letters.
The symbols of some elements
are represented by one letter and the symbols of some elements are represented
by two letters.
If the symbol has only one
letter it should be written as capital letter and if the symbol has two letters
then the first letter should be capital letter and the second letter should be
small letter.
Symbols
of some common elements :-
 |
| google image |
5) Atomic mass :-
Since atoms are very small
in size its mass is very small and determining its mass is very difficult. So
the mass of an atom is compared with the mass of a standard atom.
The atom which is considered as
a standard atom for comparing the masses of other atoms is carbon – 12 atom
whose atomic mass is 12 u (atomic mass unit).
One atomic mass unit (u) is the
mass of 1/12th the mass of a carbon – 12 atom.
The atomic mass of an element is
defined as the average mass of one atom of the element compared with 1/12th
the mass of a carbon – 12 atom.
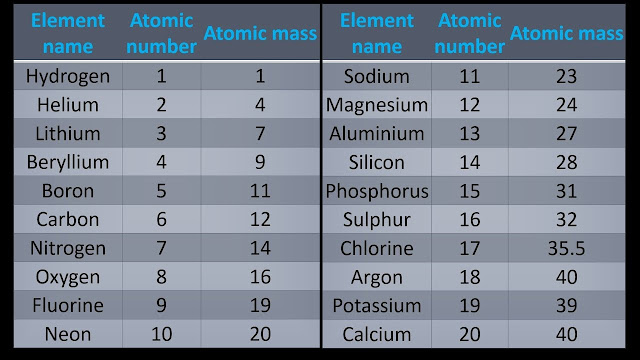
Atomic
masses of some elements :-
6) Molecule :-
A molecule is
the smallest particle of an element or compound which exists independently and
shows all the properties of that substance.
A molecule is a group of two or
more elements that are held together by attractive forces.
Atoms of the same element or
different elements can join together to form molecules.
Molecule of an element contains atoms of
the same element.
Molecules of some elements contain only one
atom and molecules of some elements contain two or more atoms.
 |
| Add caption |
Atomicity of an element :- is the number of atoms present in one molecule of the element.
Atomicity of some elements :-
ii) Molecule of compounds :-
Molecule of a
compound contains atoms of two or more different types of elements.
Molecules of some compounds :-
7) Ions :-
Compounds containing metal and non metal
elements contain charged particles called ions.
An ion is a charged particle having positive
or negative charge. A positively charged ion is called ‘cation’ and a
negatively charged ion is called ‘anion’.
Valency :- is the combining capacity of an
element.
Some common ions and
their valencies
:-
8) Writing
chemical formulae :-
i) Write the symbols / formula of the elements or ions so that the symbol of the metal or positive ion is on the
left and symbol / formula of the non
metal or negative ion is on the right.
ii) Write the valences of the elements or ions
below the elements or ions.
iii) Cross over the valences of the
combining ions.
iv) Polyatomic ions should be enclosed
in bracket before writing the formula.
Examples :-
[ TRICK TO FOLLOW: -Interchange the values
of the Valences and put at the base of
the Symbol to obtain Formula]
i) Formula of hydrogen chloride ii) Formula of hydrogen sulphide
Symbol
H Cl Symbol
H
S
Valency 1 1 Valency 1
2
Formula HCl Formula
H2S
iii) Formula
of Magnesium chloride iv) Formula of Carbon
tetrachloride
Symbol Mg Cl Symbol
C
Cl
Valency 2 1 Valency
4
1
Formula MgCl2 Formula
CCl4
v) Formula of Calcium oxide vi) Formula of Aluminium oxide
Symbol Ca
O Symbol
Al O
Valency 2
2 Valency 3 2
Formula Ca2O2
= CaO Formula Al2O3
vii) Formula
of Sodium nitrate viii) Formula of Calcium hydroxide
Symbol Na
NO3 Symbol Ca
OH
Valency
1
1 Valency 2
1
Formula NaNO3
Formula
Ca(OH)2
ix) Formula
of Sodium carbonate x) Formula of Ammonium sulphate
Symbol Na
CO3
Symbol NH4 SO4
Valency
1
2 Valency 1 2
Formula Na2CO3
Formula (NH4)2SO4
9) Molecular
mass / Formula unit mass:-
The molecular
mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a
molecule of the substance.
Molecular mass is expressed in atomic mass units (u).
Eg:-
Molecular mass of water – H2O
Atomic mass of H = I u
Atomic mass of O = 16 u
Molecular mass of H2O
= 1x2+10 = 2+16 = 18 u
Molecular mass of Nitric
acid
– HNO3
Atomic mass of H = 1 u
Atomic mass of N = 14 u
Atomic mass of O = 16 u
Molecular mass of HNO3
= 1+14+16x3 = 1+14+48 = 63 u
10) Mole
concept :-
A mole of a substance is that amount of
the substance which contains the same number of particles (atoms, molecules or
ions) that are present in 12g of Carbon – 12.
The number of particles (atoms) present
in 12g of Carbon – 12 is
6.022 x 1023
. This number is called Avagadro Number or Avagadro Constant.
A mole represents two things :-
i) It represents
a definite number of particles (atoms, molecules or ions) equal to 6.022 x 1023
.
ii) It
represents a definite mass of a substance equal to the gram atomic mass of an
element or the gram molecular mass of a compound.
Gram atomic mass
of an element :- is its atomic mass expressed in grams.
Eg
:- Gram atomic mass of Oxygen = O2 =
16 x 2 = 32g.
Gram molecular mass of a compound :- is its molecular mass expressed
in grams.
Eg
:- Gram molecular mass of water = H2O = 1 x 2 + 16 = 2 + 16 = 18g.
Relationship
between number of moles (n), mass (m), molar mass (M), Number of atoms or
molecules (N), and Avagadro number (NO).
m N m
n =
---- , n
= ---- , m = n x N , M = ---
M NO n










No comments:
Post a Comment