REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS:
Ø LIFE SPAN: Period from birth to a
natural death of an organism. Eg. Parrot- 140 years, Crow- 15 years.

Ø REPRODUCTION: Biological Process where an organism give rise to young
ones of its own kind.
Ø ASEXUAL Reproduction: Process in which Offspring (CLONES) is produced by only ONE individual; No
involvement of Gametes.
Ø SEXUAL Reproduction: Process in which Offspring (Hybrids) is produced by TWO Parents; Fusion of
male female gametes occur.
Ø CLONES: Morphologically &
genetically similar individuals. Eg. Mostly Unicellular organisms. sometimes multi cellular too. (Technically any organism produced from single parent cell, remember DOLLY)

Ø Binary Fission: mode of asexual reproduction where an individual divides
into two equal halves. Eg. Amoeba.
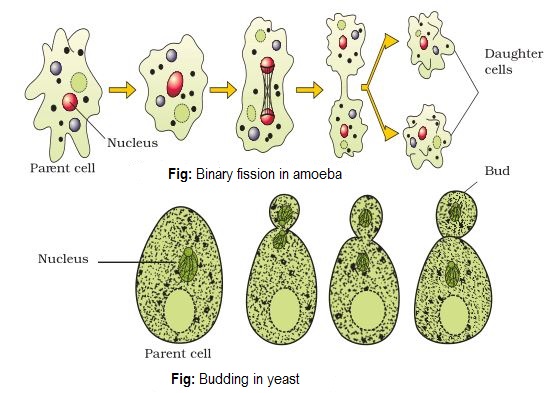
Ø Budding: Asexual reproduction
where an individual divides into two Unequal halves (small buds). Eg. Yeast.
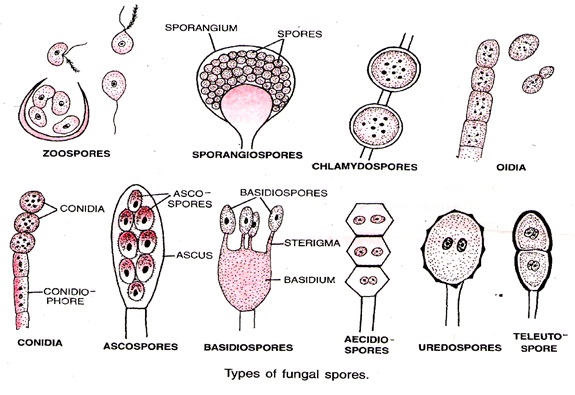
Ø Spores: Special structures for
asexual reproduction in FUNGUS: - mostly Zoospores (microscopic motile spores)
others include Conidia (non motile exospores eg. Penicillium), some animals
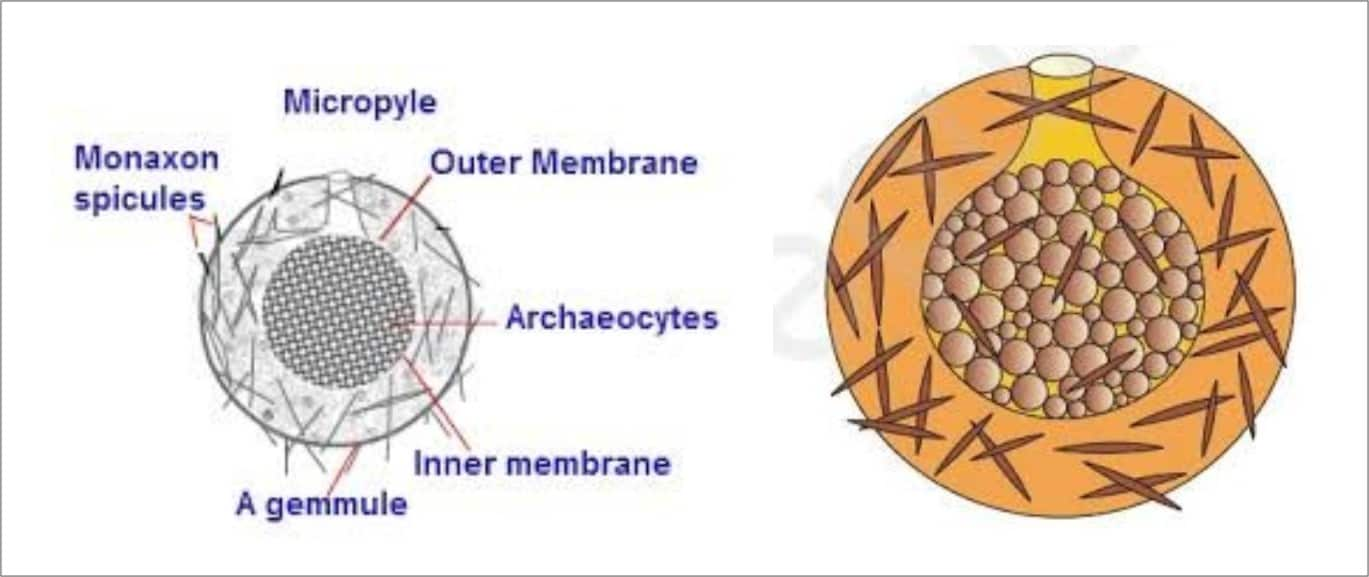
also have special structures like Exogenous & Endogenous Buds in Hydra
& GEMMULES (mostly for Perrination/ passing adverse conditions) in
Sponges.
Ø VEGITATIVE PROPAGATION-
Rhizomes (Ginger), eye
(potato), bulbils (agave), leaf bud (Bryophillum).
 |
| (Rhizome of Ginger) |
 |
| (Eye in Potato Tuber) |
 | |
| (Bulbils of Agave) |
Ø WATER HYACINTH (Terror of Bengal):- Most invasive weed in India (in Standing Water) due to Vegetative
Propagation (Stem OFFSETS).was introduced for beautiful flower & shapes of
leaves, now a Problem.
| (Offsets in Water Hyacinth) |
Ø Sexual Reproduction is favoured during Adverse conditions:-
As it is a complex & slow process as compared to asexual reproduction,
hence needs less energy (which is a point during adverse conditions).
Moreover,
it produces Variations (Hybrids) which provides better suitability & adaptability of
genes in the environment.
Ø The form of growth & maturation prior to sexual phase is
called JUVINILE/Vegetative Phase.eg. Annuals /biennials. In Perennials inter -
flowering period is present. Eg. Bamboo flowers only once in lifetime. Strobilanthus kunthiana (Neelkuranji of famous Nilgiri Hills in South) flowers once
in 12 years. (Last in Sept-Oct. 2018).
 |
| (Bamboo Flower) |
| (Neelkuranji in Munnar valley Kerala) |
Ø Females of Placental Mammals undergo cyclic changes in
Ovarian activities as well as Hormones during reproduction:- OESTRUS CYCLE (Non Primate Mammals/ seasonal breeders) eg.. Cow, sheep, rat.
Deer, dog etc.. MENSTRUAL CYCLE (Primate Mammals/ continuous breeders)eg. Human, apes,
monkeys.
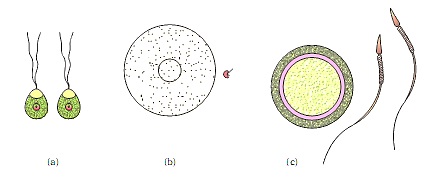
Ø GAMETOGENESIS: process of formation of reproductive cells (male/female).
(a) Isogametes /Homogametes (when gametes are same. eg. Chlymadomonas, cladophora);
(b) & (c) Anisogametes/Heterogametes (male gamete is small and motile sperm/antherozoid
& female gamete is large and non motile Ovum/Egg).
Ø SEXUALITY IN ORGANISMS: Animals with both sexes are HERMAPHRODITE (earthworm,
leech, Tapeworm). Plants are bisexual (Homothallic or Monoecious) &
Unisexual (Heterothallic or Dioecious:-Stamenate/Pistillate)
Ø GAMETIC MEIOSIS in Diploids (2n) as Meiocytes (gamete mother cell or
Gametogonia) undergoes meiosis. But Haploid parents (n) produce gametes by
Mitosis and undergo ZYGOTIC MEIOSIS to produce haploid body.
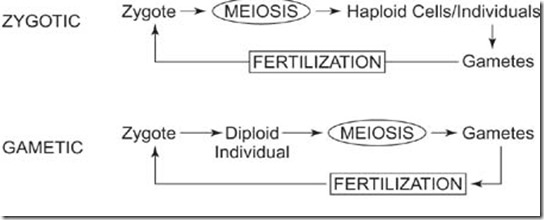
Ø Chromosomes in MEIOCYTES = 2 X Chromosomes in Gametes; eg. Human meiocyte (46) &
Gamete (23).
Ø GAMETE TRANSFER: In simple plants (algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophyta) Water is
the medium. Number of male gametes is high to increase the chance factor of
fertilization. In Angiosperms (seed Plants) Pollen Grain carry the male gamete
& Ovule carry the Female Gamete/Egg.
Ø SYNGAMY (fusion of gametes)
results in a diploid Zygote (2n). Fertilization & Syngamy are synonamus.
Ø PARTHENOGENESIS: Formation of organisms without Syngamy/ Fertilization. Eg.
Rotifers, Honeybee, Turkey.
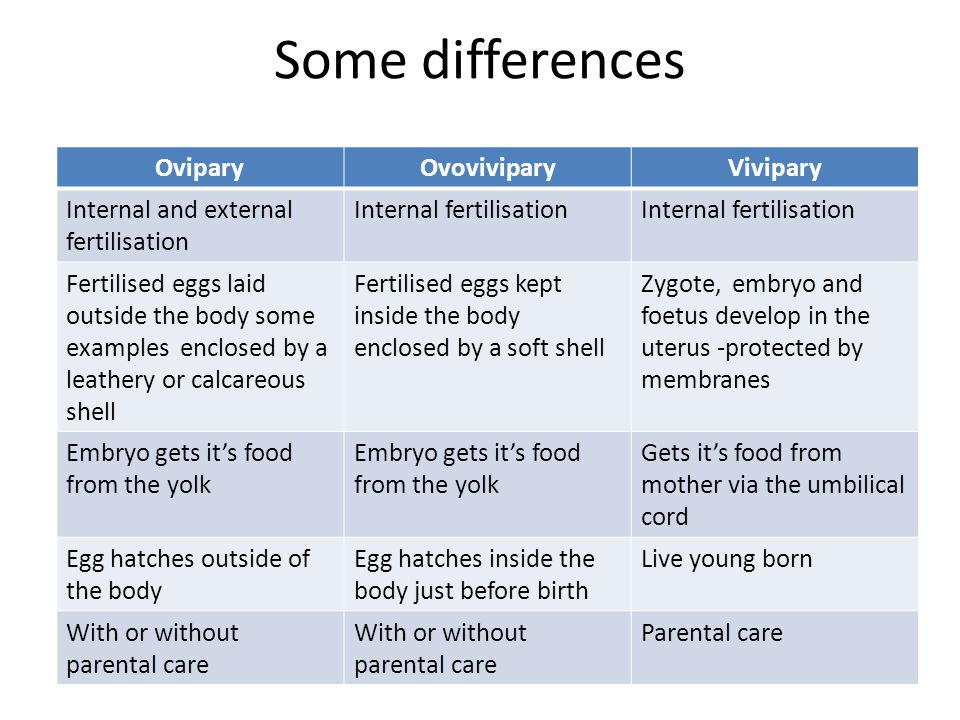
Ø ZYGOTE (Fertilized egg) is the
first stage of an embryo. Development may be outside the body eg.. egg jelly in
water like fish, frog or in Hard calcareous shells (reptiles, birds)- OVIPAROUS DEVELOPMENT (due to External Fertilization) OR development inside the
body of females and females give birth to young ones .eg. mammals like human
beings (Due to Internal Fertilization) [VIVIPARY]
REVISION & ADDITIONAL TIPS
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
·
LIFE SPAN:- life
expectancy eg. Tortoise – 150 yrs.
·
Unicellular organisms –
IMMORTAL.
·
May Fly – One Day.
·
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
(TYPES):-
v FISSION:-
(1) BINARY=
(a) SIMPLE/ASYMMETRICAL eg. Amoeba
(b) LONGITUDINAL /VERTICAL eg. Euglena; Trypanosoma
(c) TRANSVERSE/
HORIZONTAL eg. Paramecium, Planaria, Diatoms, Bacteria
(d) OBLIQUE eg.
Dinoflagellata (ceratium)
(2) MULTIPLE= ENCYSTMENT and SPORULATION ( eg. Amoeba);
SCHIZOGONY of Merozoites & SPOROGONY of Oocyst (eg. plasmodium)
(3) PLASMOTOMY eg. Multinucleate protozoa like Opalina
& Pelomyxa. [In Paramecium, nuclear division: Meganucleus- Amitosis;
Micronucleus - Mitosis ]
v BUDDING(TORULATION):-
(A) INTERNAL BUD:- Gemmules eg. All freshwater & few
marine Sponges
(B) EXTERNAL BUD:- Yeast, some Bacteria & Protozoan,
Metazoa (some Sponges & Cnidarians)
v FRAGMENTATION:-
SIMPLE (eg. Spirogyra), GEMMA (eg. Liverworts), FISSIPARITY
(eg. Echinodermata)
v REGENERATION:-
Amoeba (if nuclear material undamaged considerably);
Sponges, Planarians.
v SPORE FORMATION:-
Fungi produces two class of spores (a) SPORANGIOSPORE (ENDOSPORE) eg.
Naked, wall less non absorbent, Motile ZOOSPORES & Non Motile Aplanospore. (b) CONIDIA:
(EXOGENOUS) eg. Ascomycetes & Basidiomycetes. Two main types:- Thallic
Conidia (at Tip or Intercalary, develop by Septation & Fragmentation of
Hyphae); Blastic Conidia (develop as a chain or single spore by Budding/ Swelling
process)
v VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION:-
(A) NATURAL:-
(1) Roots (Dahlia, Sweet Potato);
(2) Stem-Tuber (eg. Potato), Stem- Bulbs ( eg. Garlic,
Daffodils, Onion), Stem-Corms (like Rhizomes eg. Colocasia, Crocus, Freesia),
Rhizome (eg. Banana, Ginger, Turmeric), Suckers (eg. Mint, Chrysanthemum), (3) Subaerial/Creeping
Stem (RUNNER:- Lawn Grass, Centella; STOLONS:- Straw-Berry, Vallisneria;
OFFSETS:- Water Hyacinth, Water Lettuce) [Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes
)called “Terror of Bengal” derive oxygen from water hence killing aquatic life,
it reproduce through offsets, runners, stolons];
(4) Aerial Stems:- Phylloclades of Opuntia
(5) Leaves (Begonia, Bryophyllum,Kalanchoe)
(6) Bulbils (Oxalis, Agave, Pineapple,Yam, Lilly, Chlorophytum)
(7) Turion (overwintering bud in some aquatic plants eg.
Utricularia, Potamogeton)
(B) ARTIFICIAL/Horticultural METHOD:-
(1) CUTTING :- Stem (eg. Rose, Sugarcane, Coleus,
Bougainvillea) Root (eg. Dahlia)
(2) LAYERING (eg. Jasmine, Rhododendron, Magnolia):- [The
branch developing adventitious roots is called LAYER] Mound Layering (Apple;
Gooseberries) Air Layering/ Gootee (Mango)
(3) GRAFTING:- Cutting of plant (scion) attached to rooted
plant (stock) eg. Mango
(4) BUD GRAFTING ( T-shaped cut; spring season) eg. Pear, Peach, Plum, Citrus, rose
(5) TISSUE
CULTURE/MICROPROPAGATION:- in vitro; explants, Callus; eg. Asparagus, Orchids,
Chrysanthemum [STEPS:- Selection; Aseptic Culture; Callus Multiplication; Shoot
Elongation; Acclimatization]
(Courtesy Google Images for all the images used here)



very helpful😊
ReplyDelete